SaaS, PaaS, IaaS: Understanding Cloud Service Models — A Comprehensive Guide
The evolution of cloud computing has been one of the most significant shifts in information technology. Among its core offerings are three primary cloud service models: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). This comprehensive guide delves into each of these models, providing an in-depth understanding of their functionalities, benefits, challenges, and real-world applications.
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Before diving into the specific models, it’s essential to grasp the basics of cloud computing. Cloud computing refers to the delivery of various services over the Internet, including data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a detailed overview of cloud computing.
Understanding the Service Models
1. Software as a Service (SaaS)
What is SaaS?
SaaS is a software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a third-party provider and made available to customers over the Internet. It is known for its accessibility and ease of use.

Benefits of SaaS
- Accessibility: SaaS applications can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Cost-Effective: It reduces the cost of software ownership and eliminates the need for hardware installation and maintenance.
- Scalability: SaaS solutions are easily scalable, allowing businesses to adjust resources based on their needs.
Challenges with SaaS
- Data Security: Since data is stored off-site, there are concerns regarding data security and privacy.
- Limited Customization: SaaS applications may not be highly customizable to meet specific business requirements.
Real-World Examples
- Google Workspace: Provides a suite of productivity and collaboration tools.
- Salesforce: A leading CRM platform offered as a SaaS.
For more on SaaS, Salesforce offers insights into its applications and benefits.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
What is PaaS?
PaaS provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app.
Benefits of PaaS
- Streamlined Development: Offers a framework that developers can build upon to develop or customize applications.
- Cost-Efficiency: Reduces the cost of purchasing and managing underlying hardware and software.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Facilitates collaborative work even when teams are remote.
Challenges with PaaS
- Vendor Lock-in: There’s a potential risk of getting too dependent on a particular provider for service options.
- Security Concerns: Since the platform is managed by a third party, there might be security vulnerabilities.
Real-World Examples
- Microsoft Azure: A leading PaaS offering various tools for building and hosting applications.
- Heroku: A popular PaaS that enables developers to build, run, and operate applications entirely in the cloud.
For further exploration of PaaS, Heroku’s website provides valuable insights.
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
What is IaaS?
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet. It offers the basic infrastructure on which to build and deploy applications and handle data storage.
Benefits of IaaS
- Flexibility and Scalability: IaaS allows businesses to purchase resources on-demand and scale up or down as required.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It eliminates the capital expense of setting up and managing an onsite data center.
- Control Over Infrastructure: While the infrastructure is hosted by a third-party, users maintain control over it.
Challenges with IaaS
- Complexity of Management: Managing IaaS requires technical expertise, particularly for handling and securing the infrastructure.
- Downtime Risks: Being reliant on the Internet means there’s a risk of downtime and service interruptions.
Real-World Examples
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Offers a broad set of global compute, storage, database, analytics, application, and deployment services.
- Google Cloud Platform: Provides a suite of cloud computing services that run on the same infrastructure that Google uses.
To learn more about IaaS, visit Amazon Web Services’ website.
Comparing SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
While these three models offer cloud-based services, they differ in terms of control, flexibility, and management level required by the users.
- SaaS: Offers ready-to-use, out-of-the-box solutions requiring minimal control or management from the user.
- PaaS: Provides a platform for development and deployment, offering more control than SaaS but less than IaaS.
- IaaS: Offers the most control, providing the infrastructure on which everything else sits.
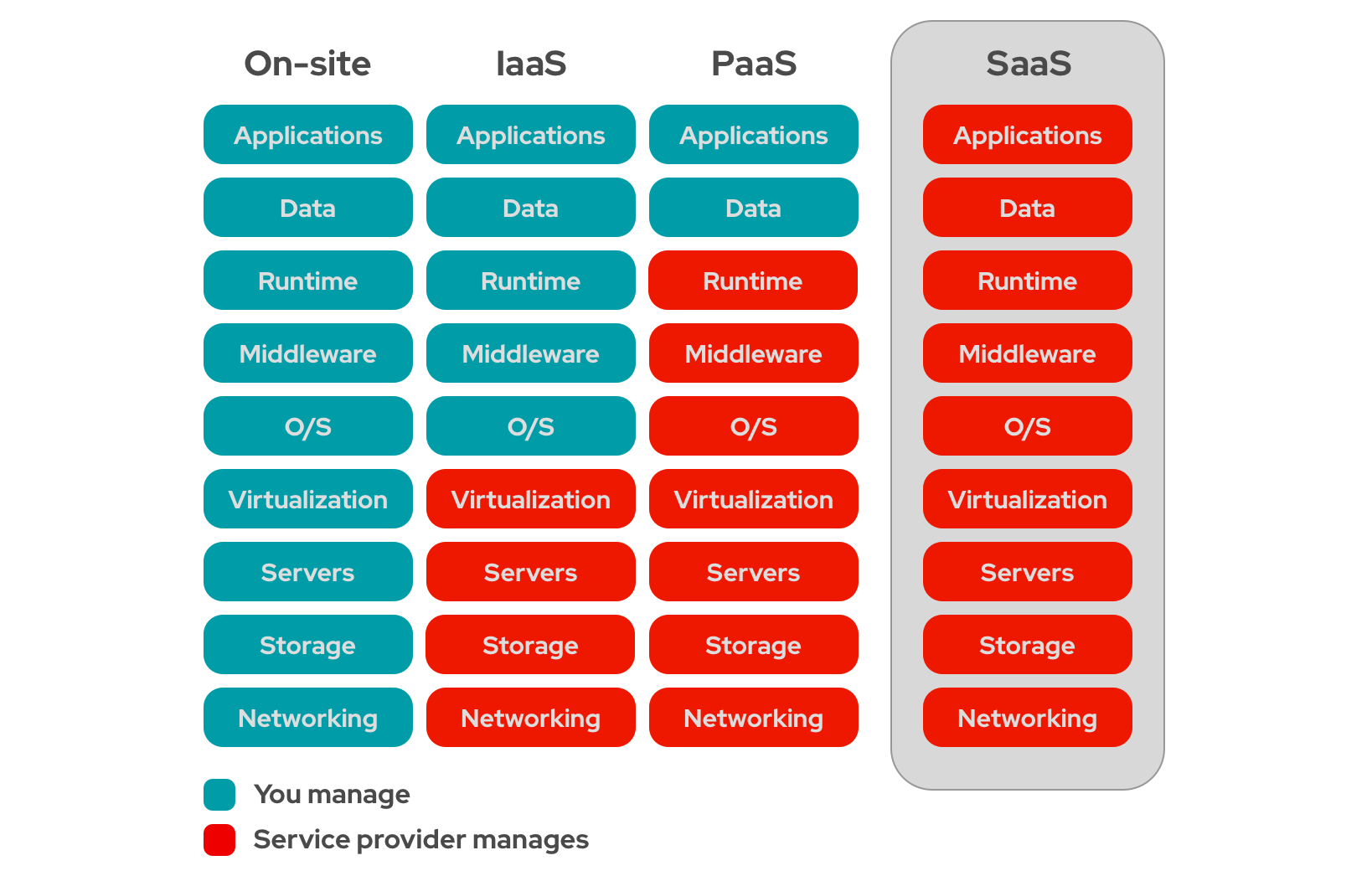
For a more detailed comparison, IBM’s cloud resource is a helpful guide.
The Future of Cloud Service Models
The future of cloud services is promising, with advancements in AI, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) driving innovation. Hybrid and multi-cloud solutions are becoming more prevalent, offering more flexibility and optimization options.
For insights into the future trends in cloud computing, Gartner’s research offers valuable perspectives.
Conclusion: Embracing the Cloud Era
The distinctions between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are crucial in understanding cloud services. As businesses continue to migrate to the cloud, recognizing which model or combination of models suits their needs is key to leveraging the full potential of cloud computing.
For a deeper understanding of how to choose the right cloud service model, Microsoft’s cloud computing guide provides a comprehensive look.


